Indoor gardening has become increasingly popular in recent years, and growing potatoes is a rewarding and practical venture for many gardeners. Potatoes are a versatile staple crop that can thrive indoors with proper care and the right containers. In this article, we will delve into the process of selecting the right containers for growing potatoes indoors, considering essential factors that will ensure a successful harvest. By understanding the key aspects of container selection, you can create an ideal environment for your potatoes to flourish, even in limited space.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Indoor Potato Growing
Before we delve into the specifics of container selection, let’s briefly explore the concept of indoor potato growing. Growing potatoes indoors allows you to have a year-round supply of fresh and flavourful tubers, especially if outdoor gardening space is limited or weather conditions are less than ideal.
When growing potatoes indoors, there are two main methods to consider:
- Traditional Soil Method: This approach involves using regular potting soil and allowing the potato plants to grow as they would outdoors. The container must provide sufficient depth for the potatoes to develop underground, and it should mimic the natural growing conditions as closely as possible.
- Hydroponic Method: In this method, potatoes are grown without soil, and their roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich water solution. Hydroponic systems can be more space-efficient and offer better control over plant nutrition.
2. Factors to Consider When Choosing Potato Containers
Selecting the right containers is crucial for the success of your indoor potato-growing project. Consider the following factors to ensure your potato plants have an optimal environment to thrive:
Size and Depth
Potatoes require ample space for their roots to grow and produce tubers. The container’s depth should be at least 12 to 16 inches (30 to 40 centimetres) to accommodate the growth of the potato plants. Additionally, larger containers will allow for multiple tubers to grow, increasing your overall yield.
Material
Containers can be made from various materials, such as plastic, ceramic, fabric, or even recycled materials. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages:
- Plastic: Lightweight and easy to clean, plastic containers are widely available. However, they might not be as breathable as other materials, leading to potential moisture retention issues.
- Ceramic: These containers offer a visually appealing option, but they can be heavy and may not have adequate drainage holes.
- Fabric: Fabric pots promote better aeration and root health. They are lightweight and easy to store when not in use, making them an excellent choice for indoor gardening.
- Recycled Materials: Repurposing items like grow bags or sturdy buckets can be a sustainable and cost-effective way to grow potatoes indoors.



Drainage and Mobility
Proper drainage is essential for preventing waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot and other fungal issues. Ensure that your chosen containers have sufficient drainage holes at the bottom. Consider the ease of moving your containers, especially if you plan to reposition them to optimise sunlight exposure or temperature conditions.
Aeration and Light Penetration
Good airflow around the potato plants’ roots is vital for healthy growth. Containers with breathable materials or air-pruning features help to promote root health and discourage root circling. Potatoes also need a significant amount of sunlight to produce healthy tubers. Choose containers that allow enough light to penetrate the soil, and position them in the sunniest spot available.
3. Types of Containers for Growing Potatoes Indoors
Now that we understand the essential factors to consider, let’s explore various container options specifically suited for growing potatoes indoors:
Fabric Grow Bags
Fabric grow bags are a popular choice among indoor gardeners due to their excellent drainage and aeration properties. They come in various sizes and are often made from breathable, durable fabric materials. The porous fabric prevents waterlogging and encourages air pruning of the roots, leading to healthier plants and increased tuber production.
Smart Pots
Smart pots are similar to fabric grow bags but are made with a sturdier, more rigid material. They offer the same benefits of excellent aeration and root health while maintaining their shape even when empty. Smart pots are available in various sizes and are an excellent option for growing multiple potato plants in limited space.
Tower Planters
Tower planters are vertical gardening systems designed for space efficiency. These tall containers feature multiple tiers, allowing you to grow potatoes on different levels. They are a great option for maximising space while still providing adequate depth for root growth.
Recycled Plastic Buckets
Sturdy plastic buckets, like those used for paint or construction materials, can be repurposed as potato containers. Ensure that you drill sufficient drainage holes at the bottom and provide enough depth for the potatoes to grow.
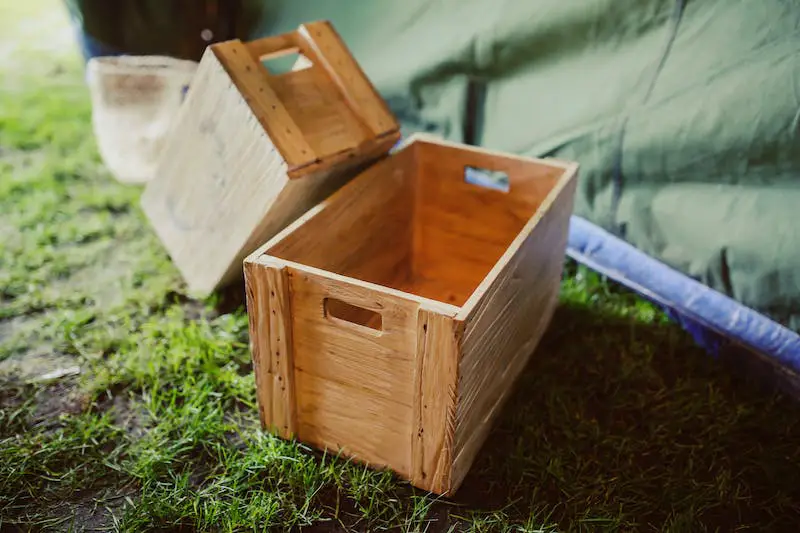
Wooden Crates or Boxes
If you prefer a rustic look, wooden crates or boxes can be used to grow potatoes indoors. Line them with a breathable fabric or plastic sheet to prevent soil from falling through the gaps while allowing for adequate drainage.
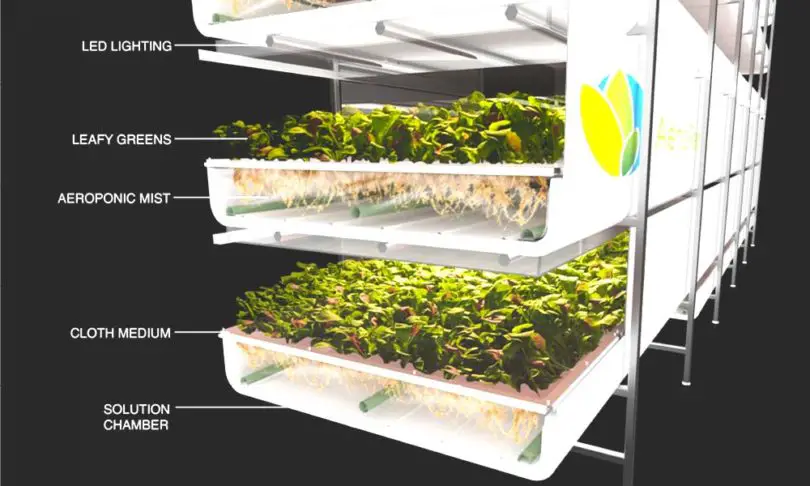
Hydroponic Systems
For a soilless approach to growing potatoes, consider hydroponic systems designed for root vegetables. These systems immerse the roots in a nutrient-rich water solution, providing precise control over plant nutrition.
4. Preparing the Containers and Planting Potatoes
Once you’ve selected the right containers for your indoor potato garden, follow these steps to prepare them and plant your potatoes:
- Prepare the Containers: Before planting, clean the containers thoroughly to remove any potential contaminants. If using recycled materials, sanitise them with a diluted bleach solution to eliminate any harmful residues.
- Add Potting Mix or Hydroponic Solution: If growing potatoes in soil, fill the containers with a high-quality potting mix enriched with organic matter. For hydroponic systems, fill the reservoir with the appropriate nutrient solution suitable for root vegetables.
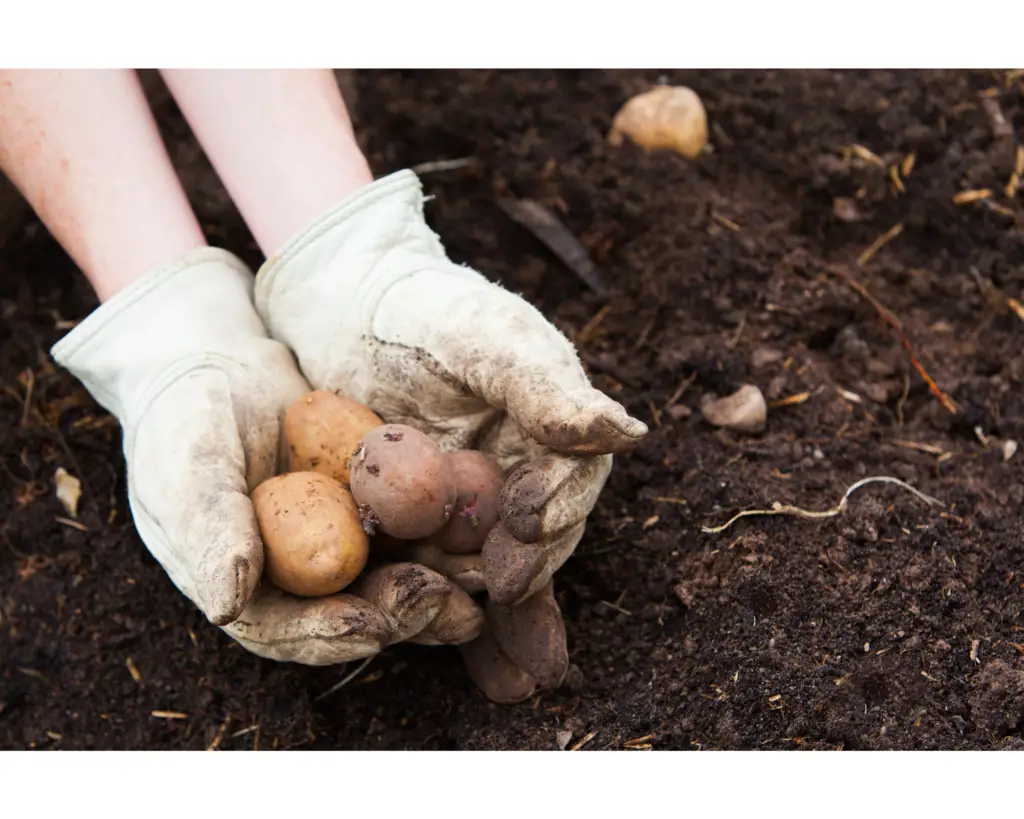
- Select Seed Potatoes: Choose certified disease-free seed potatoes from a reputable source. Larger seed potatoes can be cut into smaller pieces, each containing at least one “eye” or bud, allowing them to sprout and grow.
- Planting Process: Place the seed potatoes on top of the potting mix, spaced a few inches apart, and cover them with a few inches or centimetres of additional soil or hydroponic medium. As the plants grow, gradually add more soil or medium to ensure the tubers are adequately covered.
- Watering and Light: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Indoor potato plants require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. If natural light is insufficient, consider supplementing with grow lights to ensure proper plant growth.
- Fertilisation: Monitor your plants’ growth and provide appropriate fertilization according to the type of growing method you have chosen. For soil-based systems, use a balanced fertiliser, while hydroponic systems require specific nutrient solutions.



5. Care and Maintenance of Indoor Potato Plants
To ensure healthy growth and maximize your potato yield, pay close attention to the following care and maintenance tips:
Watering and Soil Nutrients
Potatoes prefer consistent moisture levels, so monitor the soil’s moisture and adjust your watering schedule accordingly. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can result in reduced tuber development.
Regularly check the soil for nutrient deficiencies and supplement with appropriate fertilisers as needed. For hydroponic systems, maintain the nutrient solution at optimal levels to support healthy plant growth.
Temperature and Humidity
Potatoes prefer a cooler environment with temperatures ranging between 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C) during the day and slightly cooler at night. Avoid exposing the plants to extreme temperature fluctuations, as this can stress the plants and affect tuber formation. Maintain moderate humidity levels, as excessively dry air can lead to wilted foliage and hinder plant growth.
Pruning and Topping
As the potato plants grow, they may produce lush foliage. To encourage tuber development, consider pruning some of the excess foliage to direct the plant’s energy toward tuber growth. Topping or removing the top few inches or centimetres of the plant’s greenery can also signal the plant to divert its energy downward to produce more tubers.
Pest and Disease Control
Indoor environments may not be completely immune to pests and diseases. Inspect your plants regularly for signs of common issues such as aphids, spider mites, and fungal infections. If necessary, use organic insecticides or fungicides to address any problems promptly.
Support, Pollination and Fruit Formation
As potato plants grow taller, they may need support to prevent them from toppling over. Stakes or trellises can help keep the plants upright and ensure they receive adequate light and airflow.
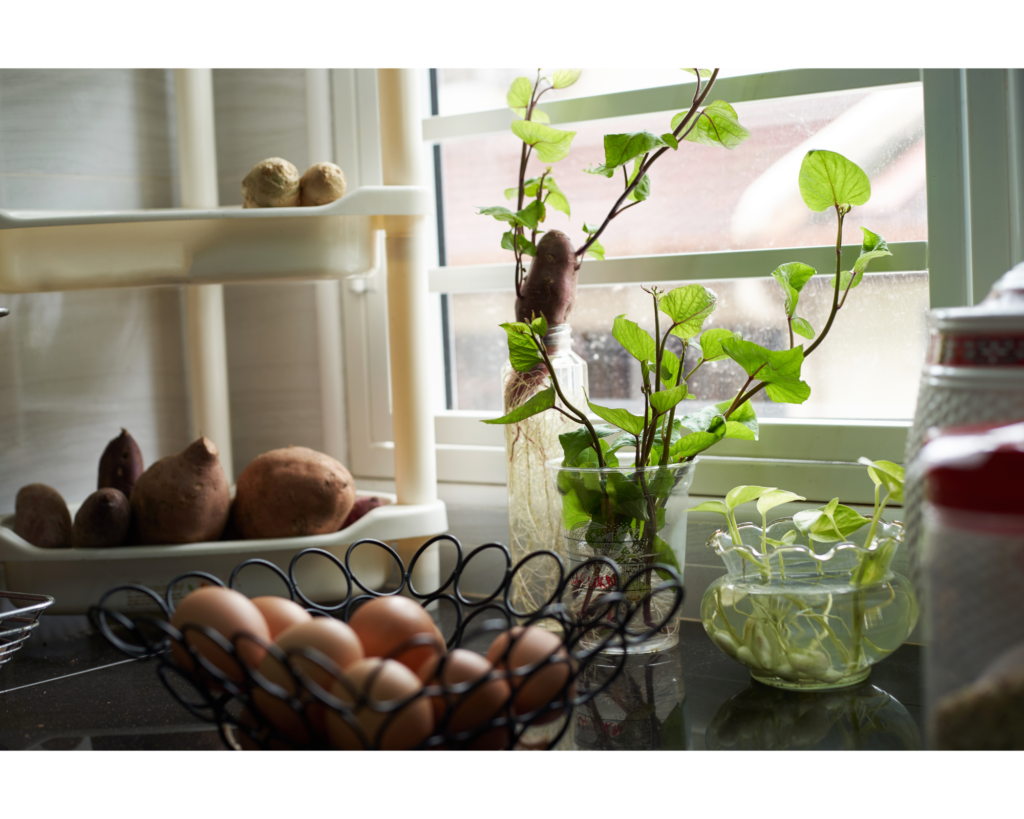
Potato plants produce flowers, but the tubers themselves are not the fruit; they are the underground stems of the plant. The flowers can be a beautiful addition to your indoor garden, but they do not play a significant role in the development of potatoes.


Harvesting
The time to harvest your indoor potatoes will depend on the variety you’ve chosen and the growing conditions. As the plants mature, they will naturally start to die back, and the foliage will turn yellow and brown. This is an indication that the potatoes are ready for harvesting. Carefully dig up the tubers from the soil or hydroponic medium and store them in a cool, dark place.
Conclusion
Growing potatoes indoors can be a satisfying and rewarding experience for any gardener. By selecting the right containers and providing proper care and maintenance, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of fresh, delicious potatoes year-round. Whether you opt for traditional soil-based methods or venture into hydroponics, understanding the specific needs of your potato plants is crucial for success. With the right containers, adequate light, proper watering, and nutrient management, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a successful indoor potato grower.
As with any gardening endeavor, patience, observation, and adjustment are essential. Take note of what works best for your indoor potato plants and be prepared to adapt your methods as needed. Happy indoor gardening and bon appétit!



